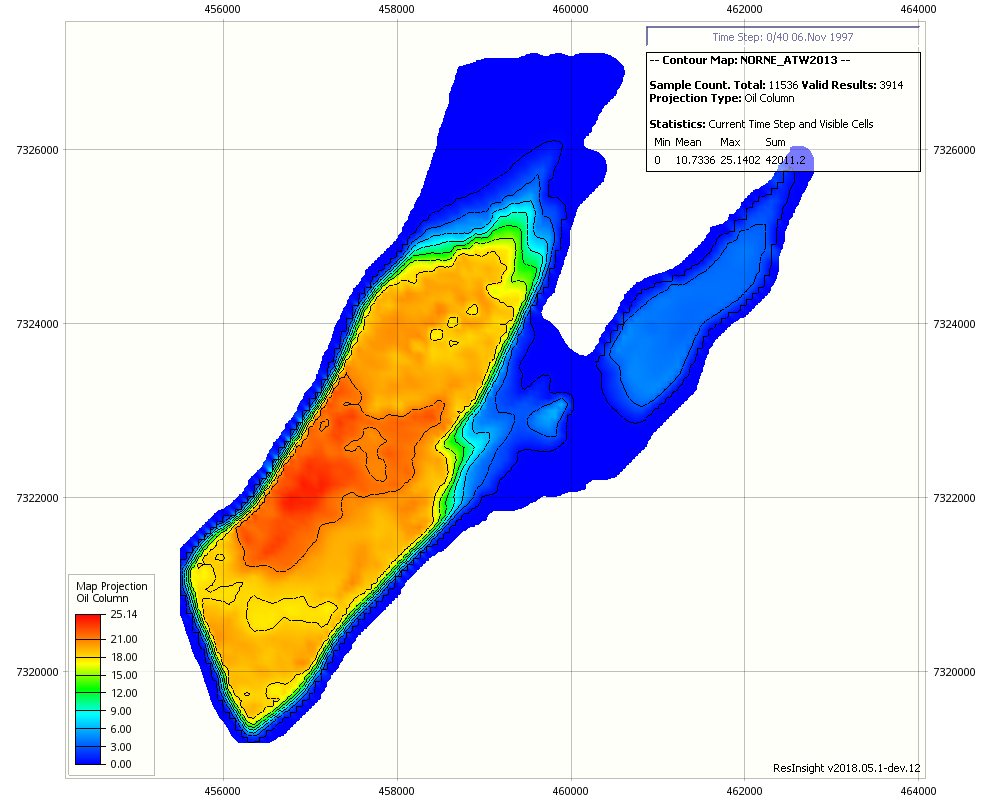
ResInsight can create contour maps based on different forms of aggregation of 3D Eclipse data onto a 2D Plane. Any 3D result value can be aggregated, in addition to specialised results, such as Oil, Gas and Hydrocarbon columns. A Contour Map is a specialised 2D view with many of the same features as the 3D views, including property filters, range filters and display of faults and wells.
Creating New Contour Maps
Contour Maps can be created in many different ways:
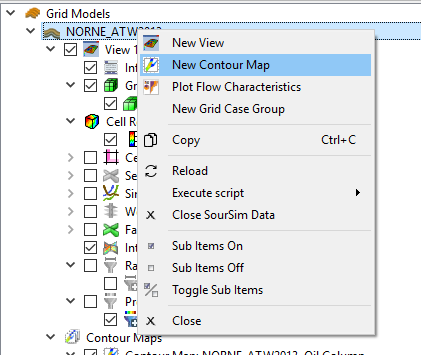
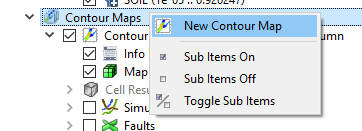
- New Contour Map from the context menu of case or the Contour Maps project tree item underneath the case. These will create contour maps with default values.
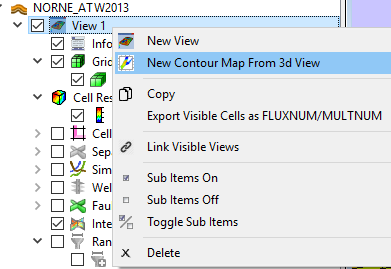
- New Contour Map from 3D View in the Eclipse View context menu. This will create a contour map based on the existing 3D View with matching filters and result.
- Duplicate Contour Map from the context menu of an existing Contour Map. This will copy the existing map.
Properties of the Contour Maps
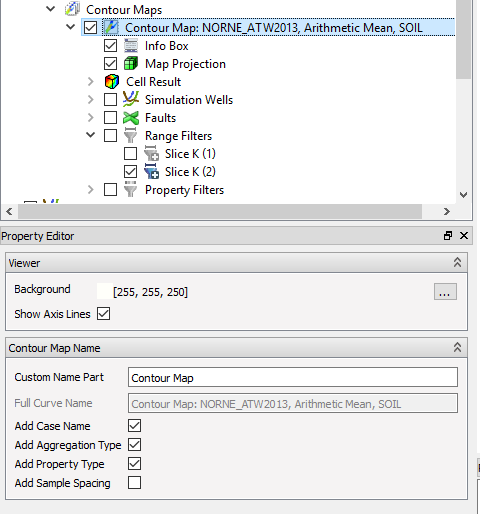
A contour Map has many of the same options available as a 3D View, but is always orthographic/parallel projection with no perspective projection or lighting available. Instead of the 3D Grid Box, the Contour Maps uses a 2D Grid simular to the 2d Intersection Views with optional Axis Lines controlled with the Show Axis Lines toggle. The name of the map can be automatically generated from the Case Name, Property Type, Aggregation Type and Sample Spacing (See Map Projection Properties for the two latter).
Map Projection Properties
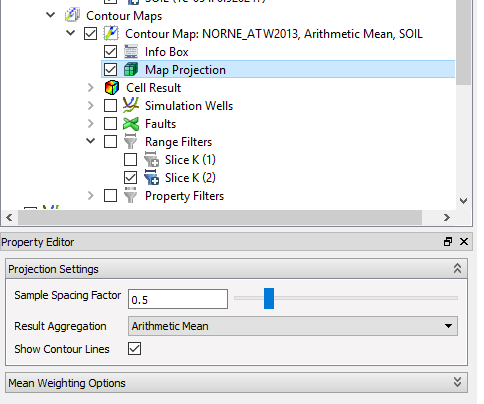
The Map Projection settings control how the 3D Data is aggregated onto the 2D plane. In all cases the results are calculated for a square 2D Cell lying in an arbitrary z-plane of the 3D Grid. For each 2D cell a cuboid extrusion in the full bounding extent of the 3D grid is created and this cuboid extrusion is used to calculate the volume of intersection with the 3D Grid cells for all volume weighted sums and averages. For the regular sums, a vertical ray through the center of the 2D cell is used instead. Since the ray may travel through multiple cells in the same K-layer, all the values from within one K-layer are averaged before being added to the sum.
A set of parameters governs this projection:
- The first option Sample Spacing Factor controls how many 2D Grid Cells are used in the map. The factor is multiplied by the characteristic cell length/width of the 3D grid to get the 2D Cell Size. A smaller factor will thus create a finer Contour Map.
- The second option Show Contour Lines toggles on/off the contour lines in the view.
- The final control in the Projection Settings box is the Result Aggregation. Here the following options are available:
| Aggregation Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Oil Column | A sum of SOIL * NTG * PORO * dZ |
| Gas Column | A sum of SGAS * NTG * PORO * dZ |
| Hydrocarbon Column | A sum of (SOIL + SGAS)* NTG * PORO * dZ |
| Arithmetic Mean | A volume weighted arithmetic mean of the specified cell result |
| Harmonic Mean | A volume weighted harmonic mean of the specified cell result |
| Geometric Mean | A volume weighted geometric mean of the specified cell result |
| Volume Weighted Sum | A volume weighted sum of the specified cell result. Suitable for volume fractions such as SOIL or PORO |
| Sum | A sum of the specified cell result. Suitable for absolute quantities. |
| Top Value | The first value encountered downwards vertically |
| Min Value | The minimum cell result value in the volume underneath the 2D Element |
| Max Value | The maximum cell result value in the volume underneath the 2D Element |
For the Column options, no Cell Result is available in the property tree under the Contour Map.
Weighting Means by Cell Result
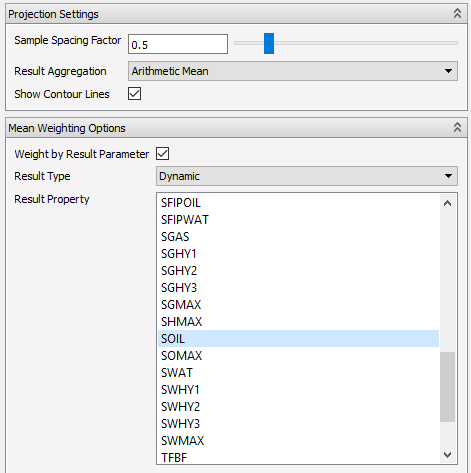
For the Arithmetic Mean, Geometric Mean and Harmonic Mean it is also possible to specify a cell result as a weighting parameter in addition to the regular weighting by volume of intersection. The total weight will then be the volume of intersection multiplied by the specified cell result. The full range of regular cell results is available for this use.