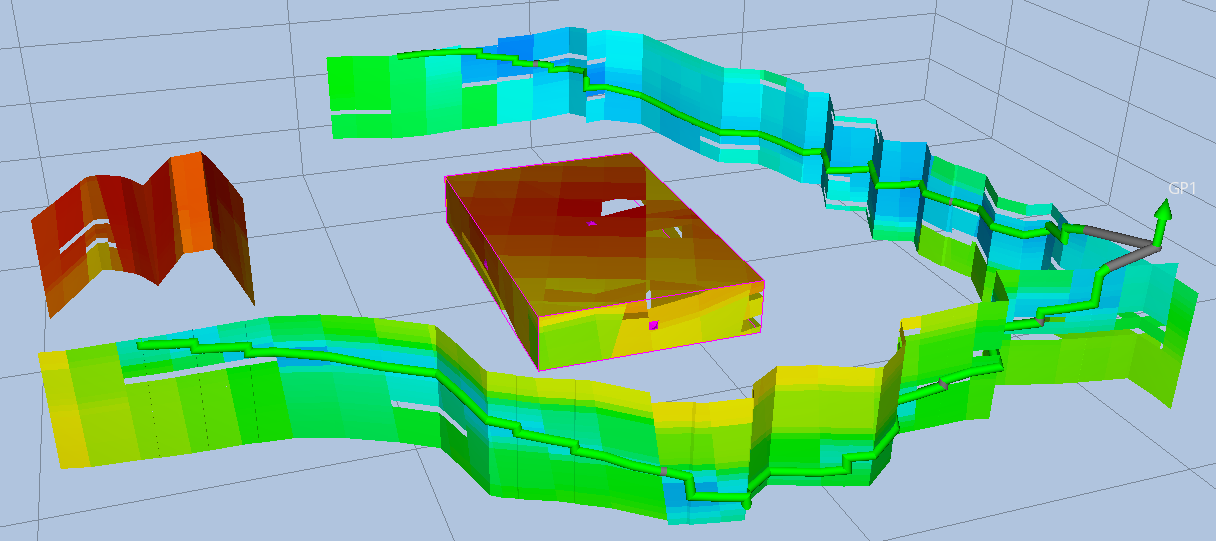
Intersections are cross sections of the grid model that displays the grid cell values on planes that cut through the grid in various ways.
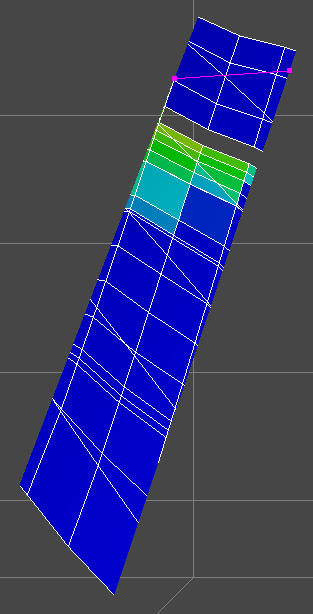
There are two main types of intersections. The first one which simply is called Intersection, is defined by a piece-wise linear curve and an extrusion direction. The curve can be either a Simulation Well, a Well Path, a user defined polyline, or a user defined line. These intersections can also be shown in their own separate 2D Intersection View
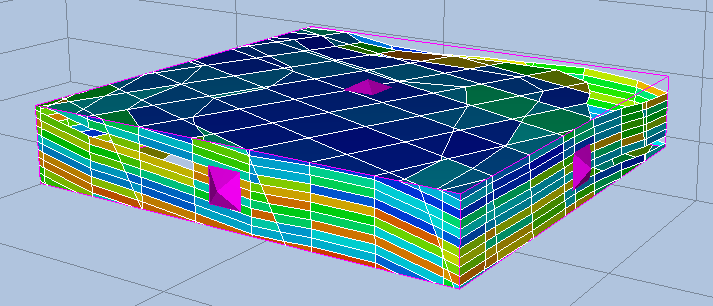
The second intersection type is called an Intersection Box. An Intersection Box can be used as a box cutting the grid cells, or collapsed to a restricted axis aligned plane.
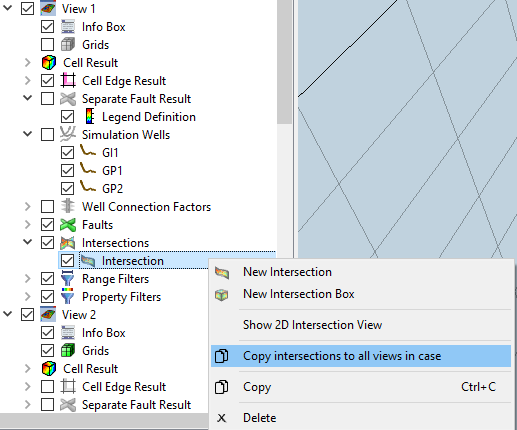
All types of intersections are stored in a folder named Intersections in a View as shown below. Once created, the intersections may be copied to other views by selecting the Copy intersections to all views in case option from the context menu of each intersection.

Once created, the intersections may be copied to other views by selecting the Copy intersections to all views in case option from the context menu of each intersection.
Curve Based Intersections
There are four types of curve based intersections: Well Path, Simulation Well, Polyline, and Azimuth and Dip. Azimuth and Dip differs from the other three curves, as it is defined just by one straight line. It is called Azimuth and Dip because the plane’s extrusion direction can be defined by the two angles.
Any of these intersections can be created by activating 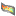 New Intersection from the context menu of the Intersections item in the Project Tree.
New Intersection from the context menu of the Intersections item in the Project Tree.
They can also be created from the context menu in the 3D view, as described below.
Common Curve Based Intersection Options
The property panel of a well path based intersection is shown below:
- Name – Automatically created based on the item specifying the intersection. The user can customize the name by editing, but will be updated if you change the well or well path.
- Intersecting Geometry – These options controls the curve to be used for the cross section, and depends on the type of intersection you choose.
- Direction – Horizontal, vertical or defined by two points.
- Extent Length – Defines how far an intersection for well path or simulation Well is extended at intersection ends.
- Show Inactive Cells – Controls if inactive cells are included when creating the intersection geometry.
Direction
The direction defined is used to extrude the curve in the defined direction, and thereby create a set of planes.
When selection the Horizontal option, the start and end point of the curve is used as a baseline, and the horizontal direction is thus perpendicular to that line.
When Defined by two points is the active option, the user can define the direction based on any two points. The direction from the first to the second point defines the extrude direction.
- The background color of this list is set to light pink when adding points by picking in the 3D view is active.
- To finish adding points, click the button Stop picking points in the Property Editor.
- The background color of the point list is then set to white.
Well Path Intersection
A new Well Path intersection can be created by right-clicking the well path in the 3D view or in the Project Tree.

When a well path intersection is created, the source well path can be changed by using the Well Path selection combo box in the Property Editor.
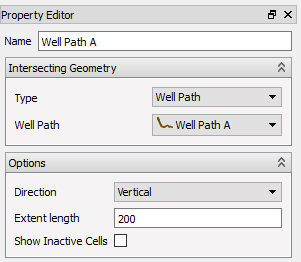
Simulation Well Intersection
A new Simulation Well intersection can be created by right-clicking the simulation well in the 3D view or in the Project Tree.
When a simulation well intersection is created, the source simulation well can be changed by using the Simulation Well selection combo box in the Property Editor.
If the well contains more than one branch, the intersection geometry will be created for the selected branch in the Branch combo box.
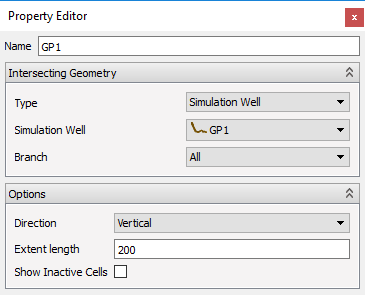
Polyline Intersection
A new Polyline intersection can be created from the context menu in the 3D view. Then, by left-clicking on reservoir geometry, a polyline is created. The points are added to the point list in the Property Editor.
- The background color of this list is set to light pink when adding points by picking in the 3D view is active.
- To finish adding points, click the button Stop picking points in the Property Editor.
- The background color of the point list is then set to white.
The points in the list can be deleted and edited using the keyboard. To append more points (by clicking in the 3D view), push the button Start picking points again.
The points in the list can be copied to clipboard using CTRL-C when keyboard focus is inside the point list. A new list of points can be pasted into the point list by using CTRL-V.
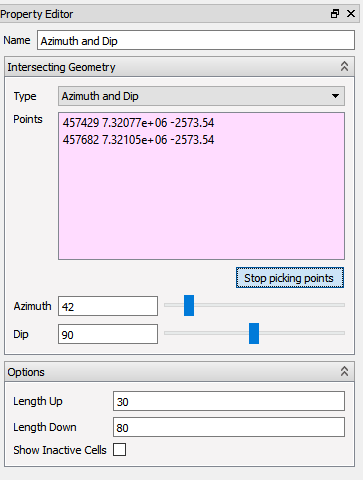
Azimuth and Dip
A new Azimuth and Dip intersection can be created from the context menu in the 3D view. Then, by left-clicking two points on reservoir geometry, a single line is created between the first point, and the second point projected down to the plane with same z-value as the first point. The two points are added to the point list in the Property Editor.
- The background color of this list is set to light pink when adding points by picking in the 3D view is active.
- To finish adding points, click the button Stop picking points in the Property Editor.
- The background color of the point list is then set to white.
The points in the list can be deleted and edited using the keyboard. To append more points by clicking in the 3D view, push the button Start picking points again.
The points in the list can be copied to clipboard using CTRL-C when keyboard focus is inside the point list. A new list of points can be pasted into the point list by using CTRL-V.
When two points are picked, a plane between the points will appear in the 3D view, with a 90 degrees Dip, and the Azimuth angle calculated from the two points. The two angles can be edited in the Property Editor of the intersection, and is defined by the following:
- Dip is the angle between the horizontal plane and down.
- Azimuth is the angle between North and the plane. Changing the azimuth will rotate the plane about the first point picked in the 3D view.
The length of the plane can also be set manually in the Property Editor.
- Length Up is the distance from the user defined horizontal line, to the top of the plane intersecting the model.
- Length Down is the distance from the user defined horizontal line, to the bottom of the plane intersecting the model.
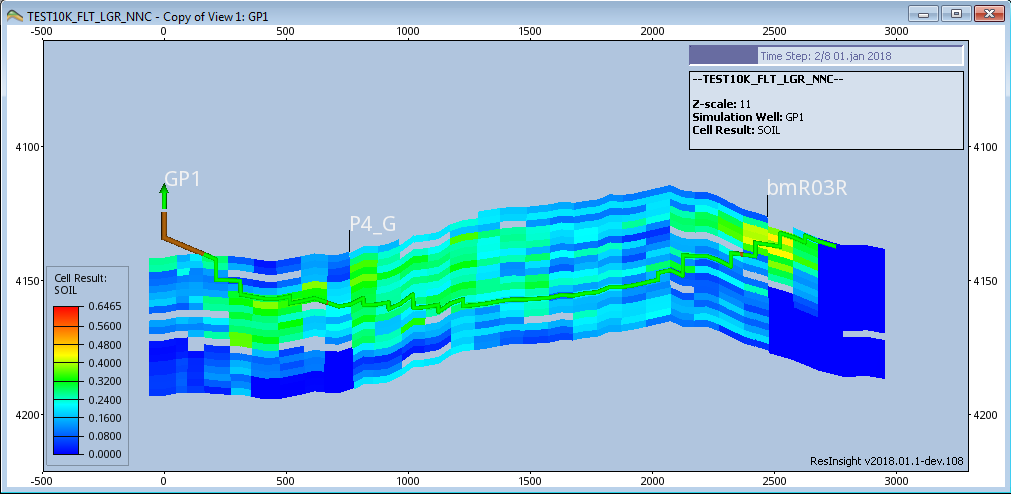
2D Intersection Views
A 2D Intersection View displays the intersection in a separate 2D view along with the defining curve. The intersection and the defining well path, simulation well or polyline is flattened to make it easier to see the intersected grid and how the well traverses it.
Each of the curve based intersections have a corresponding 2D Intersection View. Management of these views are automatic. They will be created and deleted along with the intersection.
The view can be shown either by right clicking the intersection and select the command Show 2D intersection View, or by toggling the view in the project tree directly.
Scales along the edges of the view show the depth and the horizontal length of the intersection. The length is measured from the start of the wellpath or the well head of a simulation well.
The view is mostly controlled by the options in the 3D view where the intersection is defined. There are, however some independent controls, like drawstyle, timestep and Z-scale.
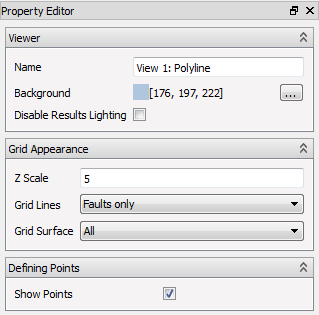
- Viewer
- Name – User editable name of the view. The default name is set by combining the name of the origin view and the intersection name.
- Background – Color of the viewer background
- Disable Results Lighting – Toggle the light effect. When the lighting is turned off, the colors are easier to compare with the legend, but the colors carry no visual cue to visualize the 3D shape. The effect is tiny on 2D Intersection Views.
- Grid Appearance – Controls the drawstyle of the grid geometry
- Z Scale – Scales the view in Z(depth) direction to make slim K-layers easier to see
- Grid Lines – Controls what mesh lines to draw
- All – All mesh lines are drawn
- Faults Only – Only mesh lines associated with faults are drawn
- None – Mesh lines are not drawn at all
- Grid Surface – Controls what grid surface geometry to draw
- All – All grid faces are drawn
- Faults Only – Only faces that are included in a fault is drawn
- None – Do not draw any faces
- Defining Points
- Show points – Toggle the display of the defining points for Polyline or Azimuth and Dip intersections.
These options are similar to the options for a regular 3D view (See View Properties )
Intersection Box and Intersection Planes
A new Intersection Box or Intersection Plane can be created from the context menu in the 3D view or the context menu in the Project Tree.
The following list describes the properties for an Intersection Box:
- Name – Automatically created based on the item specifying the intersection
- Box Type – Box or x-plane, y-plane or z-plane
- Show Inactive Cells – Controls if inactive cells are included when creating the intersection geometry
- X Coordinates – Coordinates for x range
- Y Coordinates – Coordinates for y range
- Depth – Coordinates for depth range
- XY Slider Step Size – Defines how much the value changes when the slider for XY values is changed, default value 1.0
- Depth Slider Step Size – Defines how much the value changes when the slider for depth values is changed, default value 0.5
Direct interaction in a 3D view is activated when Show 3D manipulator is pressed. Handles are displayed at the sides of the intersection object, and interactive modification is done by dragging a handle in the 3D view.